Mycena galericulata
Mycena galericulata
Description
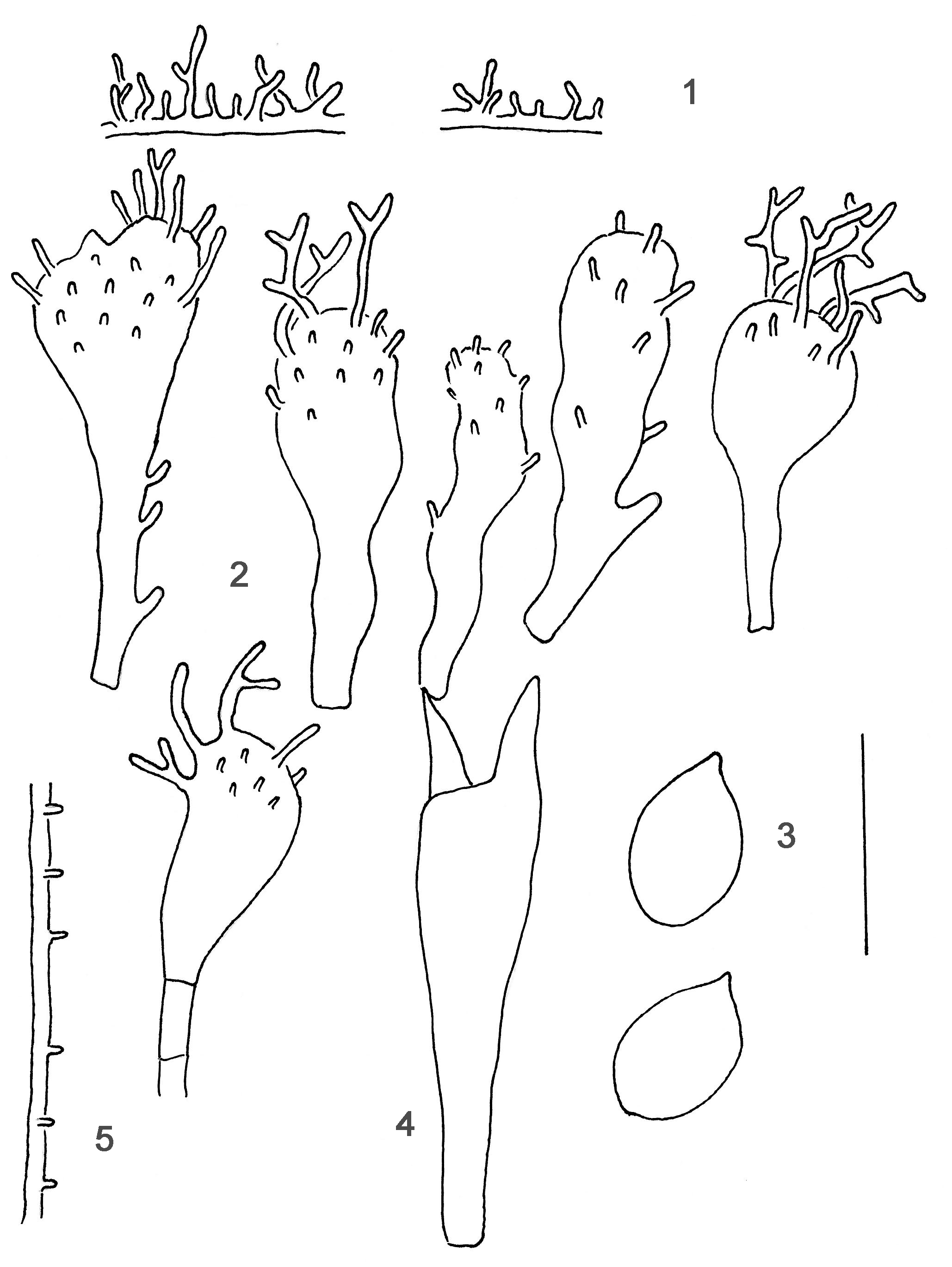
1. Hyphae of the pileipellis, 2. Cheilocystidia, 3. Spores, 4. Basidium, 5. Hypha of the cortical layer of the stem.
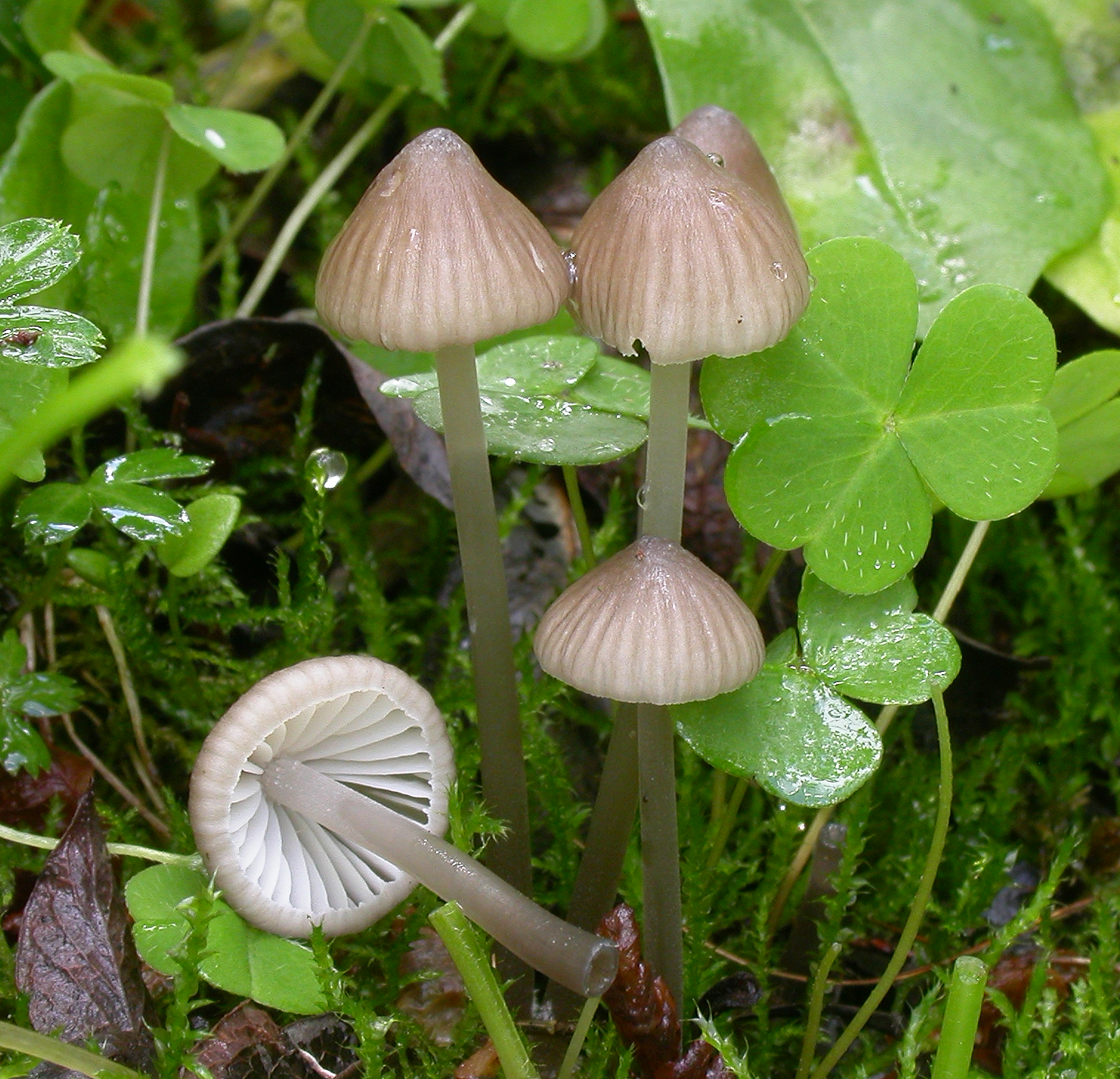
Cap 20 - 60 mm across, broadly conical, parabolical, convex to applanate, mostly with a prominent,broad umbo, sulcate to conspicuously rugose, translucent-striate, glabrous, in young stages often pale to fairly dark date brown, becoming beige to grey-brown, usually sepia brown at the centre, and often whitish at the margin. Gills 25 - 32 reaching the stem, sometimes anastomosing or furcate and sometimes dorsally intervenose with age, elastic-tough, adnate to emarginate, sometimes decurrent with a short tooth, white, not infrequently turning pale incarnate to pink. Stem 45 - 110 x 1.5 - 5 mm, , cartilaginous, elastic-tough, equal or somewhat broadened below, terete or compressed, glabrous, very dark sepia brown in young specimens, becoming grey-brown, the apex often pale grey to whitish, darker grey brown below, the base usually covered with coarse, whitish fibrils, rooting into the substratum. Odour indistinctive or somewhat disagreeable. Taste farinaceous. Basidia 33-55 x 8-10 µm, clavate, 2- or 4-spored, with sterigmata up to 10 µm long. Spores 10-12 x 7-9 µm (2-spored) or 9-12 x 6-7 µm (4-spored), Qav = 1.2-1.7, broadly pip-shaped, amyloid. Cheilocystidia 17-50 x 7-18 µm, forming a sterile band, clavate to more or less irregularly shaped, often with new heads apically, covered with few to fairly numerous, unevenly spaced, cylindrical, simple to branched, more or less curved excrescences 2-25 x 1-2 µm. Pleurocystidia absent. Lamellar trama dextrinoid. Hyphae of the pileipellis 2-2.5 µm wide, sparsely to densely diverticulate, with excrescences up to 10 µm long, simple to very branched, forming dense masses. Hyphae of the cortical layer of the stem 2-3 µm wide, sparsely covered with cylindrical excrescences 2-5 x 1 µm. Clamps abundant in the 4-spored form.
Ecology and distribution
Solitary to fasciculate on stumps, on fallen branches, mostly from hardwood trees (e.g. Fagus, Quercus, Betula and Alnus) but also on conifers. Late spring to late autumn. Very common in most of the area covered, thinning out to the north.