Mycena clavicularis
Mycena clavicularis
Description
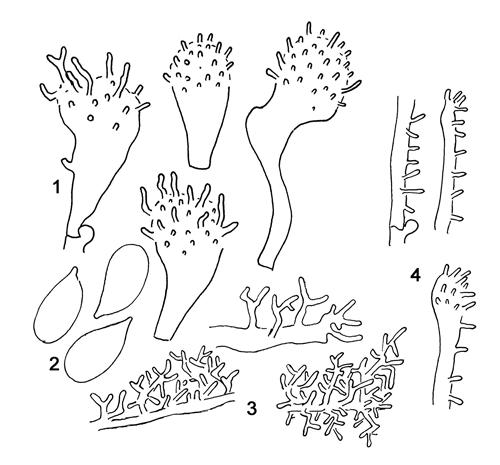
1. Cheilocystidia, 2. Spores, 3. Hyphae of the pileipellis, 4. Hyphae of the cortical layer of the stem with terminal cell.
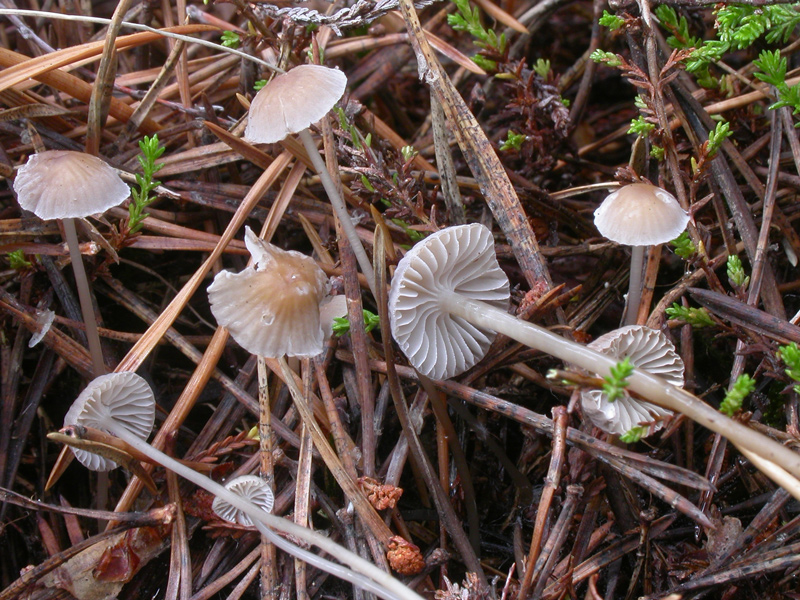
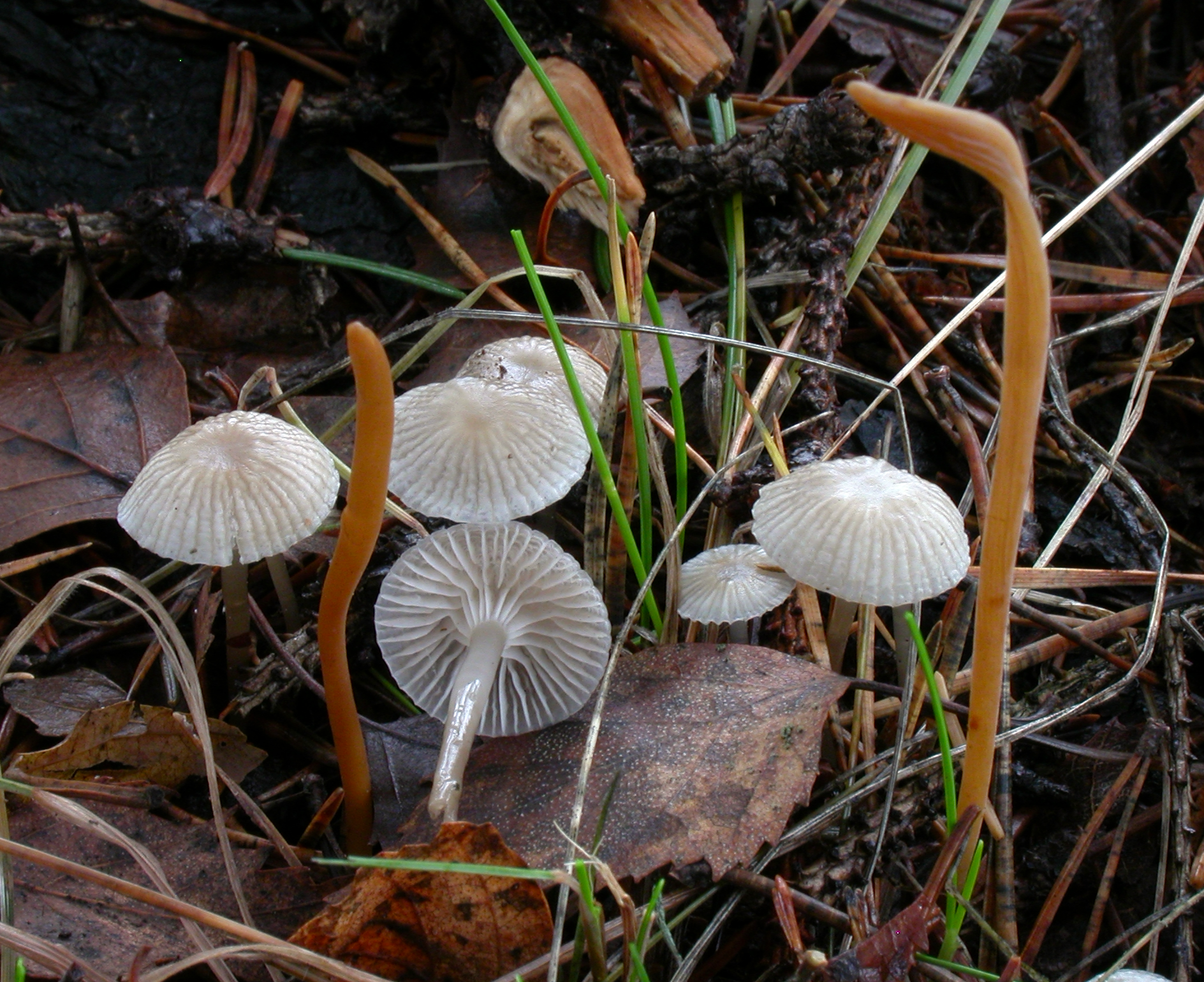
Cap 7-15 mm across, hemispherical to parabolical, flattening with age, often somewhat depressed at the centre or with a low umbo, glabrous, sulcate, translucent-striate, lubricous, pale brown to brown, darker at the centre, often sepia brown at the centre and grey-brown towards the margin. Gills 16-20 reaching the stem, broadly adnate to somewhat decurrent, with age somewhat rugulose and dorsally intervenose, white, grey-white to pale brownish. Stem 20-60 x 1-2 mm, cylindrical, equal or at times somewhat wider at the apex, cartilaginous, delicately pruinose above, glabrous for the greater part, shiny when dry, glutinous when wet, sometimes with a slimy coating, grey to brown or yellowish brown, paler to whitish above, darker towards the base that is covered with white fibrils. Odour none. Basidia 22-27 x 7-8 µm, slenderly clavate, 4-spored, with sterigmata up to 7 µm long. Spores 7.0-9.0 x 4.0-5.0 µm, pip-shaped, amyloid. Cheilocystidia 13-30 x 6-11 µm, forming a sterile band, clavate, short- to long-stalked, covered with narrow to fairly coarse, short to longer, straight to curved, cylindrical excrescences. Pleurocystidia similar. Lamellar trama dextrinoid. Hyphae of the pileipellis 2-5 µm wide, embedded in gelatinous matter, covered with simple to branched, cylindrical excrescences, tending to form dense masses. Hyphae of the cortical layer of the stem 2-3 µm wide, embedded in gelatinous matter, sparsely to densely covered with cylindrical excrescences up to 4 µm long, the terminal cells 3-5 µm wide, sparsely to densely diverticulate. Clamps present in all tissues.
Ecology and distribution
On needle beds and among debris of coniferous trees, particularly Pinus on poor soils. It can be found from May to late autumn. It is generally a rather rare species but can locally be quite common.